Government of Tamil Nadu -Teachers Recruitment Board
Name of the Post:Lecturers in Government Polytechnic Colleges and Special Institutions (Engineering / Non Engineering)
Pay Scale: Rs. 56100 – 177500 ( Level 22 )
Vacancies (Civil) :112 posts
Age Limit : Candidates should not have completed 57 years as on 01/07/2019 as per G.O. (Ms) No.156 Higher Education (B1) Department Dated: 15/09/2014.
Educational Qualifications: B.Tech/B.E/B.ARCH degree with not less than 60% or equivalent
Exam Pattern: The Computer based examination will consist of a single paper of 3 hours duration with 150 MCQs.
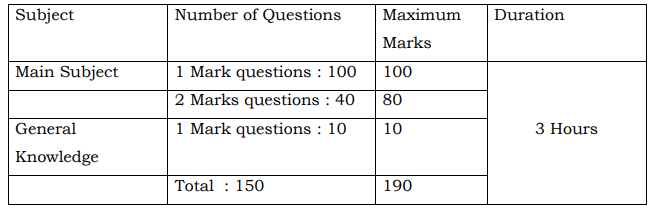
Selection Procedure : The selection will be based on two successive stages viz.
a. Computer based examination;
b. Awarding Weightage marks during Certificate Verification;
Exam Syllabus (CIVIL ENGINEERING)
UNIT 1: ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS
Linear Algebra — matrix algebra, linear equations, – eigen values and eigen vectors. Calculus- Functions of single variable, limit, continuity and differentiability – mean value
theorems, evaluation of definite and improper integrals – partial derivatives, total derivative – maxima and minima – gradient, divergence and curl – vector identities –
directional derivatives – line, surface and volume integrals – stokes, gauss and green’s theorems.
Differential equations — first order equations (linear, nonlinear) — higher order linear differential equations with constant coefficients – Cauchy’s and Euler’s equations —
initial and boundary value problems — Laplase transformations and equations — solutions to one dimensional heat and wave equations. Complex variables — analytic functions — Cauchy’s integral theorem — Taylor and Laurent series — Fourier series — general, odd and even functions. Probability and Statistics – probability and sampling theorems- conditional probability — mean — median, mode and standard deviation — random variables — Poisson, Normal
and Binomial distributions. Numerical Methods — numerical solutions of linear and non-linear algebraic equations — integration by trapezoidal and simpson’s rule, single and multistep methods for differential equations.
UNIT 2: MECHANICS
Simple stress and strain relationships in one, two and three dimensions — principal stresses, stress transformation — mohr’s circle — properties of surfaces —
friction — principle of conservation of energy — impulse and momentum — relative motions – bending moment and shear force in statically determinate beams—
simple bending theory — flexural and shear stresses — unsymmetrical bending — shear center — pressure vessels (thin and thick walled) — uniform torsion—
springs — buckling of columns —combined and direct bending stresses —theories of failure — shear stress, strain energy and distortion energy theories — residual stresses.
UNIT 3: STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
Analysis of statically determinate and indeterminate trusses — arches — cables and
frames — deflections of statically determinate structures (beams, frames and trusses) —
analysis of statically indeterminate structures (slope deflection, moment distribution
methods) — matrix methods of structural analysis — influence lines for determinate and
indeterminate structures.
UNIT 4: CONCRETE STRUCTURES
Concrete technology — properties of concrete — mix design — working stress and limit state design concepts — design of all structural components (slab, beam, column,
foundation and stair case) — retaining walls — water tanks — basic elements of prestressed concrete — methods – analysis of beams at transfer and service loads —
seismic load analysis — theory of vibration — seismology — response of structures — design methodology – all related IS codes.
UNIT 5: STEEL STRUCTURES
Connections – analysis and design of tension, compression members, beams and beam columns — trusses – column bases — plate girders — plastic analysis — wind load
analysis-all related IS codes.
UNIT 6: SOIL MECHANICS
Soil classification — engineering properties — three phase system — relationship and interrelationship — permeability — seepage — effective stress principle — consolidation —compaction — shear strength — CBR — Safe bearing capacity determination.
UNIT 7: FOUNDATION ENGINEERING
Sub surface investigation — sampling — standard penetration test — plate load test — earth pressure — effect of water table — layered soil — stability of slopes — foundation types and design requirements— stress distribution and settlement analysis — shallow and deep foundations.
UNIT 8: FLUID MECHANICS AND MACHINES AND HYDROLOGY
Properties of fluid — principle of conservation of mass — momentum — energy and corresponding equations — potential flow — Bernoulli’s equation it and application
— laminar and turbulent flow — flow in pipes — network — concept of boundary layer — uniform and non uniform flow — specific energy concept — hydraulic jump
— forces on immersed bodies — flow measurements in open. channels and pipes dimensional analysis and hydraulic modeling — impact -kinematics of flow — velocity
triangles — pumps and turbines. Hydrologic cycle — rainfall — evaporation — infiltration — stage discharge relationships— unit hydrographs — flood estimation — reservoir capacity — reservoir and channel routing well hydraulics.Duty — delta — estimation of evapo—transpiration — crop water requirements — design of lined and unlined canals — waterways — head works — gravity dams and spill ways— design of permeable foundation — types of irrigation system — irrigation methods — water logging and drainage.
UNIT 9: WATER SUPPLY AND WASTE WATER DISPOSAL
Quality standards — basic unit processes and operations – water treatment — drinking water standards — water requirements — surface water treatment — distribution —
sewage and its treatment — quantity and characteristics of waste water — primary,secondary and tertiary treatment— effluent discharge standards — domestic waste water
treatment — quantity and characteristics — treatment unit operations and unit processes — sludge disposal. — types of pollutants — their sources and impacts —standards and limits.
UNIT 10: HIGHWAY ENGINEERING
IRC standards — geometric design of highways — materials — construction and maintenance — testing and specifications of materials — design of flexible and rigid pavements — traffic characteristics — theory of traffic flow — intersection design — traffic signs and signal design — highway capacity — importance of surveying — principles and
classification — mapping — coordinate system — map projections — measurements of distance and directions — leveling — theodolite traversing —errors and adjustments —
curves.