TSPSC AE:
TSPSC stands for Telangana state public service commission
Tspsc recruits Civil engineers in AE cadre into various Departments like RWS, R and B , Irrigation , GHMC, Public health through common examinations for all posts.
Recruitment Board : TSPSC Board
Mode of examination : Online with virtual Calculator
Pay scale: Rs. 31,460-84,970/-(RPS-2015)
ELIGIBILTY :
Education Qualification:
A degree in B.E. Civil or Mechanical of a University established or incorporated by or under a Cental Act, State or Provincial Act or Institution recognized by the University Grants Commission; or
2. B.Sc. (Engg.) Degree of the Benaras Hindu University; or
3. A pass in sections ‘A’ and ’B’ of the AMIE (Ind.) Civil Examination.or
4. L.C.E. Diploma or any other equivalent Diploma of any recognized Institute;
Age:18-44* years
EXAM Pattern:
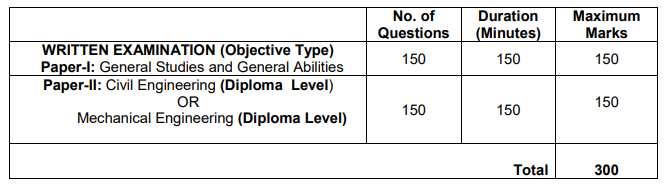
Previous Weightage:
Syllabus:
Paper-I: GENERAL STUDIES AND GENERAL ABILITIES
1. Current affairs – Regional, National and International.
2. International Relations and Events.
3. General Science; India’s Achievements in Science and Technology.
4. Environmental issues; Disaster Management- Prevention and Mitigation
Strategies.
5. Economic and Social Development of India and Telangana.
6. Physical, Social and Economic Geography of India.
7. Physical, Social and Economic Geography and Demography of Telangana.
8. Socio-economic, Political and Cultural History of Modern India with special emphasis on Indian National Movement.
9. Socio-economic, Political and Cultural History of Telangana with special emphasis on Telangana Statehood Movement and formation of Telangana state.
10. Indian Constitution; Indian Political System; Governance and Public Policy.
11. Social Exclusion; Rights issues such as Gender, Caste, Tribe, Disability etc. and
inclusive policies.
12. Society, Culture, Heritage, Arts and Literature of Telangana.
13. Policies of Telangana State.
14. Logical Reasoning; Analytical Ability and Data Interpretation.
15. Basic English. (8th Class Standard)
PAPER-II: CIVIL ENGINEERING (DIPLOMA LEVEL)
1. Surveying
Fundamental concepts; Classification of Surveys; Chain Surveying; Compass Surveying; Levelling and Contouring; Theodolite Surveying; Tacheometry; Curves; Introduction and fundamental concepts of electronic measuring instruments – EDM, Total Station, GIS & GPS.
2. Construction Materials & Practice
Properties and uses of construction materials – Stones, Bricks, Tiles, Sand, Cement, Timber, Plastics, Glass, Asbestos, Paints, Distempers, Enamels and Varnishes; Preparation of Cement mortar for various works.
Classification of Buildings as per NBC, Site investigation for foundation as per NBC -Trial Pit and auger boring, classification of foundations, construction of spread footing and well foundation; Stone and Brick masonry – types and principles of construction; Doors and Windows – types, fittings and fastenings, types and functions of Lintels, Sunshades and Roofs, Flooring – Construction and types of material; Types of Stairs; Scaffolding; Types of Plastering, Pointing, Painting and White / Colour Wash.
3. Engineering Mechanics and Strength of Materials
Forces – types of Forces, Parallelogram, Triangle and Polygon Law of Forces, Lami’s theorem; Centre of Gravity and Moment of Inertia; Simple stresses and strains, Hooke’s law – stress strain diagram, working strength, elastic constants, Poisson’s ratio, Relationship between elastic constants, compound rods, temperature stresses, strain energy, proof resilience, impact loading; Shear force and bending moment diagrams for simply supported, over hanging and cantilever beams, relation between intensity of loading, shear force and bending moment; Theory of simple bending, modulus of section, moment of resistance,
distribution of shear stress in rectangular, circular and I-Sections; Deflection in cantilever and simply supported beams subjected to simple loading; Columns and struts – Euler’s and Rankine’s formulae, Slenderness ratio, simple built-up columns; Analysis of dams and retaining walls; Simple plane and pin-jointed trusses, Stresses by method of joints and method of sections.
4. Hydraulics
Properties of fluids, fluid pressure and its measurement; Types of flows, energies in fluid motion, Bernoulli’s theorem and its applications – venture metre, pitot tube; Orifice and mouthpiece; Notches and weirs; Flow through pipes, hydraulic gradient line and total energy line, laminar and turbulent flow in pipes – Reynolds number, measurement of velocity; open channels; Water turbines – classification, centrifugal and reciprocating pumps; Layout of hydroelectric power plant.
5. Quantity Surveying
Abstract estimate, detailed estimate – centreline and long & short wall method, various items of Civil Engineering works as per Indian Standards; General Specifications – earth work, brick / stone masonry in cement mortar, RCC, plastering in cement mortar, Floor finishes with ceramic tiles and marbles, white washing, colour washing; Standard schedule of rates, lead and lift, preparation of lead statement; Computation of earth work – Midordinate, Mean Sectional area, Trepezoidal method, Prismoidal Rule; Approximate estimate – Plinth area and cubic rate estimate.
6. Design of Structures (RCC and Steel)
RCC structures: Design philosophies – principles and concepts of working stress method and limit state method, loads and permissible stresses, IS specifications, analysis and design – rectangular beam, slab, T-beam, column, footing and stair case.
Steel Structures: Properties of steel sections, loads and permissible stresses, IS specifications, Analysis and design – welded joints, beam, column, column base, tension member; Design of roof truss.
7. Irrigation Engineering
Definitions, duty, delta, base period, rainfall and its measurement, factors affecting runoff, methods of computing maximum flood discharge; Classification of head works, component parts of a weir and barrage, factors influencing selection of site – reservoirs and dams; Classification of canals, canal lining, cross drainage works; Soil erosion, water logging, soil water plant relationship; Necessity of irrigation – advantages and disadvantages, irrigation methods.
8. Environmental Engineering
Basics of ecosystem, water supply scheme; Sources of water; Conveyance of water pipes, joints and laying; Testing of water, drinking water standards; Treatment of water;
Distribution of water; Water supply connection to a building. Quantity of sewage, surface drains, design of sewers running half full, limiting velocities; Laying of sewers, sewer appurtenances; Collection of sewage samples, characteristics of domestic and industrial sewage – BOD, COD; Sewage treatment, septic tank & soak pit, sewage disposal – dilution and sewage farming; House drainage arrangements in buildings; Solid waste – collection and disposal; Air Pollution – sources, effects and controlling methods.
9. Transportation Engineering
Alignment of roads – plain and hilly terrain, surveys; Cross section of road structure, width of pavement, Camber, Gradient, Super elevation, Transition curves, horizontal and vertical alignment; Pavement marking, traffic signs, traffic islands. Types of soil, classification of soil – Textural, IS Classification, physical properties –
plasticity, cohesion, consolidation, compaction, permeability, compressibility, soil moisture content, specific gravity, density; Bearing capacity of soil.
Previous Cutoffs:
Preparation Strategy ::
Previous Notification and recruitments:
https://www.tspsc.gov.in/preview.tspsc?fileName=DIRECTRECRUITMENTNOTI/092012AE.pdf&filePath=dbPath
Previous Questions: